Sub-sectors and domains covered by the EO4GEO project
The sector covered by EO4GEO employs and develops Earth Observation (EO) and Geographical Information (GI) technologies including remote & in-situ sensing, global positioning & navigation, spatial data infrastructures, data assimilation, geospatial analysis & modelling techniques, web cartography, etc., in a strong application-centric manner.
This new emerging EO*GI sector requires cross-cutting technical and managerial skills to handle geospatial technologies, in particular to:
- manage, transform and publish geospatial data
- process, integrate and analyse them, in order to derive new, application and user-oriented information
- present and visualise information products
The EO4GEO Blueprint is tackling present and future skills, knowledge and competences in at least three areas: (1) Data acquisition and sensing (active and passive remote sensing, buoys, weather stations, drones, data logging, positioning systems, human-based sensing, geotagged social media data, mobile phone data, volunteered GI, etc. ). (2) Data assimilation by geospatial technologies, incorporating non-spatial, statistical information (e.g., land ownership, air pollution, population characteristic, …) to produce added-value geospatial information products and services; (3) Application context and wider societal relevance in supporting policy implementation, process monitoring and impact assessment.
The following application domains directly benefit from EO*GI tools and services:
- Urban and spatial planning (smart cities)
- Real estate and building management (including indoor navigation)
- Environmental monitoring (land, ocean, air quality)
- Water and groundwater management
- Tourism and management of cultural heritage
- Management of assets and underground infrastructure
- Forest management, protected sites
- Agriculture (precision farming, food quality and security)
- Climate change (impact, mitigation)
- Hazard and disaster management
- Energy resources and raw materials
- Transport and mobility (multimodal transports)
- Safety and security (border monitoring, population displacement conflict mitigation)
- Public health
With the geospatial lens, there are strong links to more generic emerging digital technologies such as IoT, Digital Twins, data cubes, artificial intelligence, computer vision, machine learning, micro- and on-board sensor technology, immersive visualisation (virtual and augmented reality), etc.
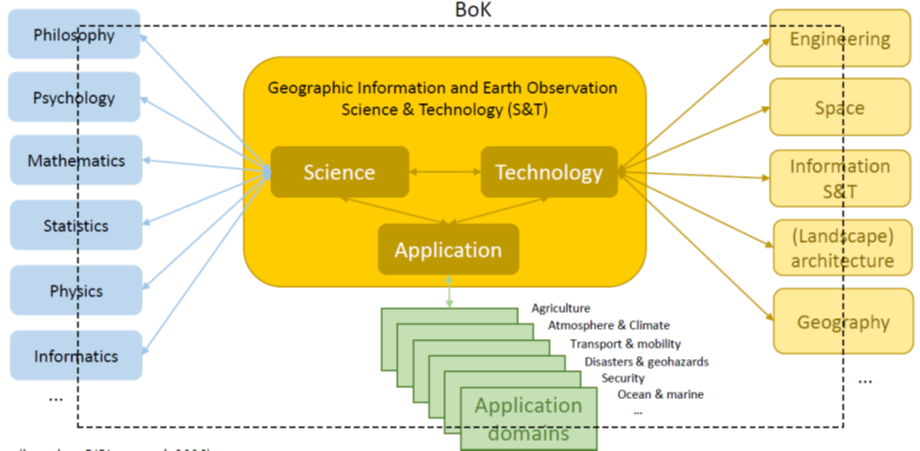
By its nature the use of space geo-information data and derived information services is cross-sectoral with ties to “Digital” and “Space” from a technological perspective but tied as well to many of the other industrial ecosystems from an application point of view. The schema below visually demonstrates this cross-sectoral nature of Earth Observation, Geographical Information and geospatial technologies.
Moreover, this document from EARSC describes the markets user needs from other business sectors and its relation with EO services.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Keep yourself updated, receive SPACE4GEO Alliance news and info on new opportunities.
Join the SPACE4GEO Alliance
Be part of the SPACE4GEO Alliance and let’s discuss and work together on the supply and demand of skills in the EO/GIS sector. Stakeholders in the EO, GIS and Skills sectors are more than welcome!
Join a Network pooling together expertise from academia, VET providers, company, public institutions, research centres and sectoral associations with the common goal of fostering skills development in the space and geoinformation downstream sector.